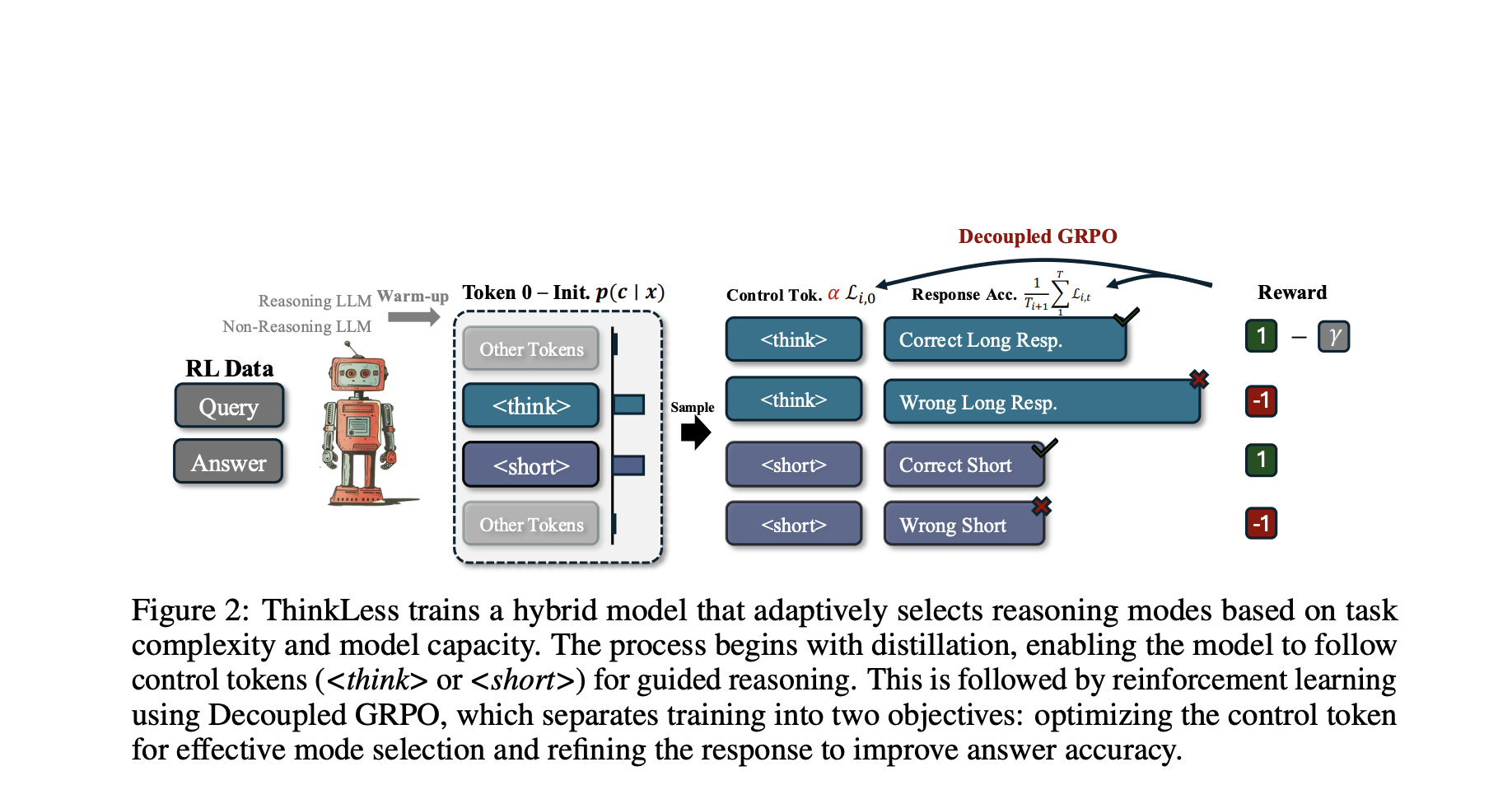
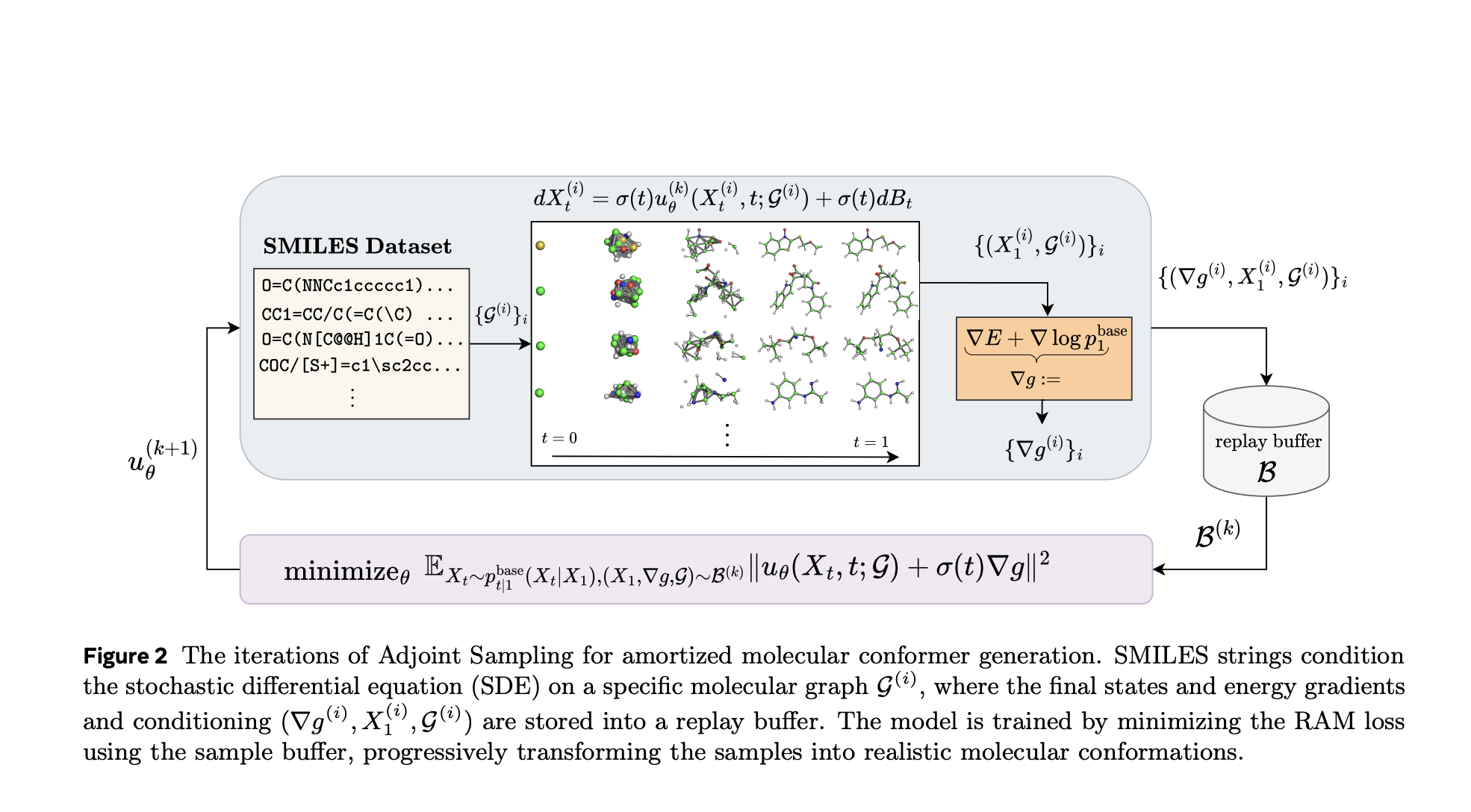
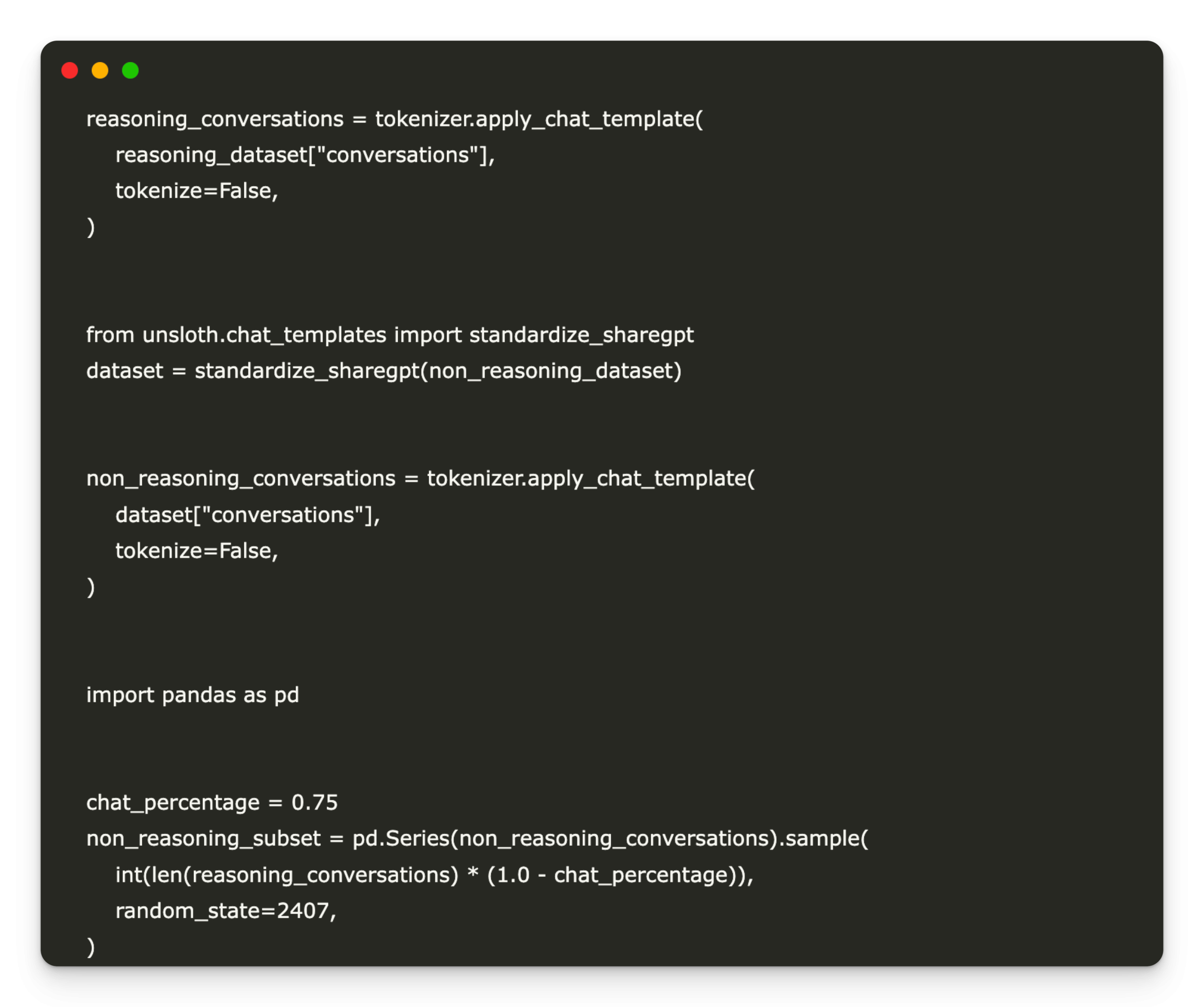
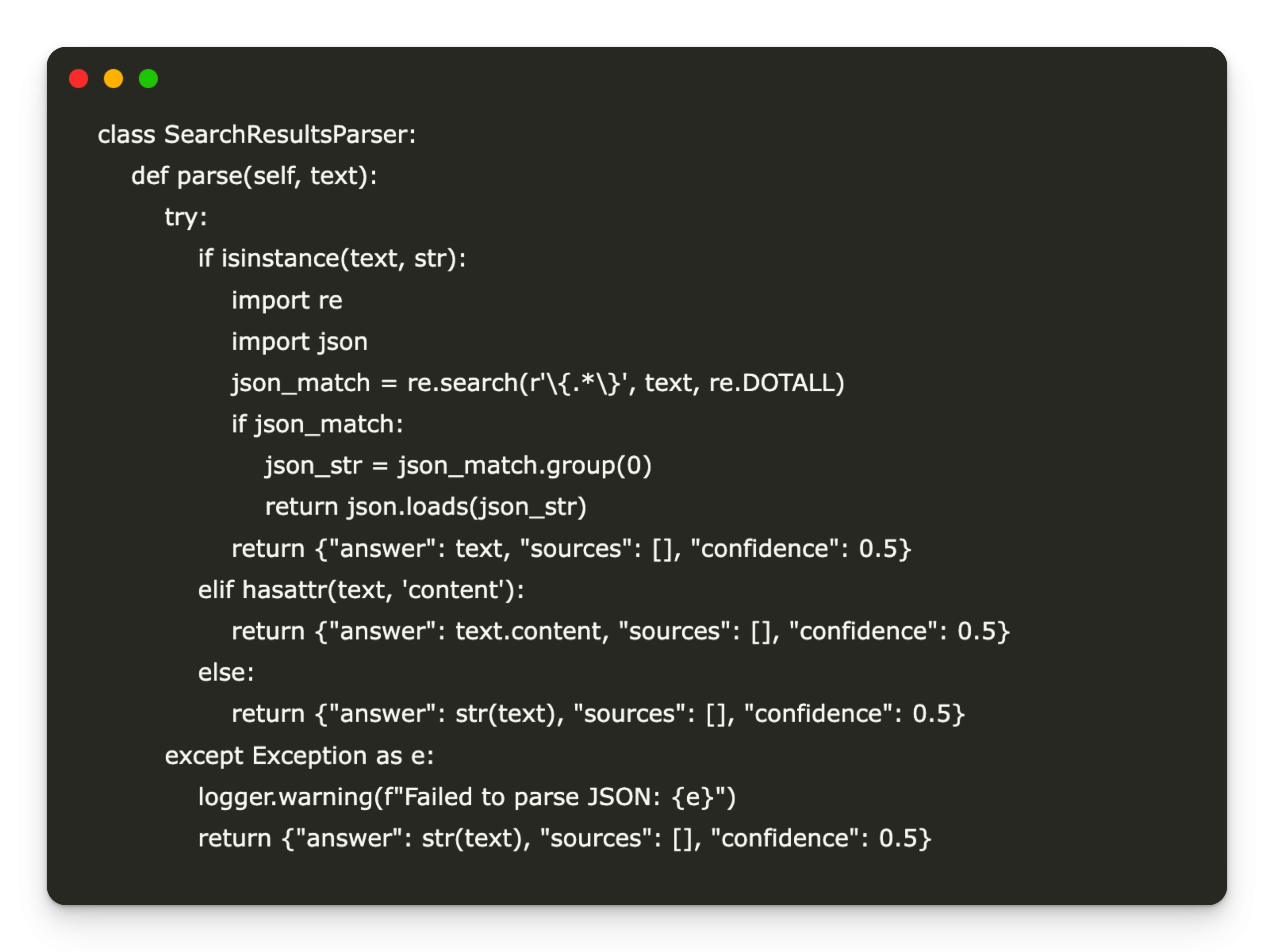
Step-by-step guide to creating synthetic data using Synthetic Data Vault (SDV)
Data in the real world are often expensive, cluttered and limited by privacy rules. Synthetic data offers a solution – and they are already widely used: LLMS Train on AI-Generated Text Fraud systems simulate edge cases Vision models prior to fake images SDV (Synthetic Data Vault) is an open source Python library that generates realistic … Read more