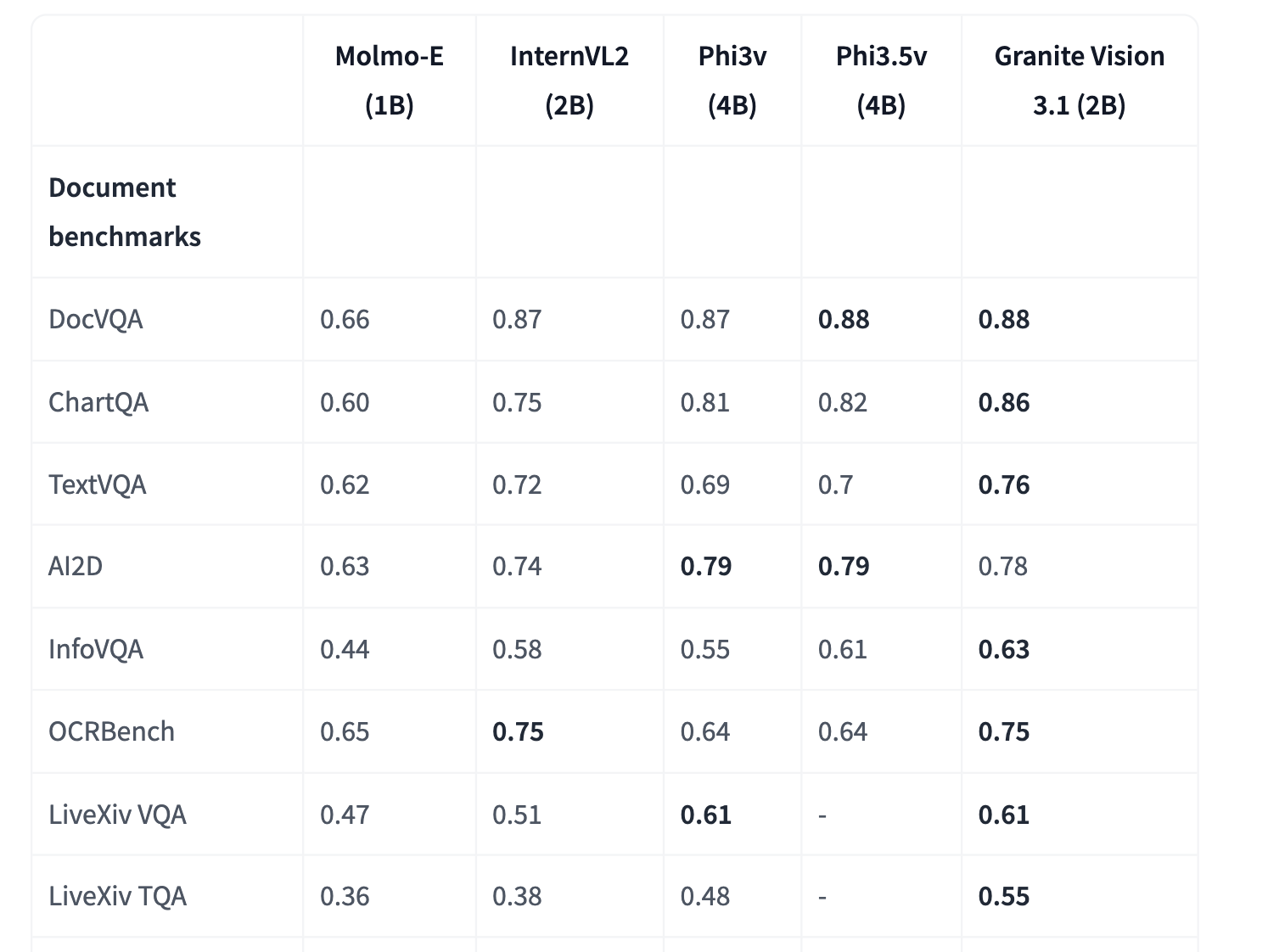
IBM AI releases Granite-Vision-3.1-2B: A small vision language model with super impressive performance on different tasks
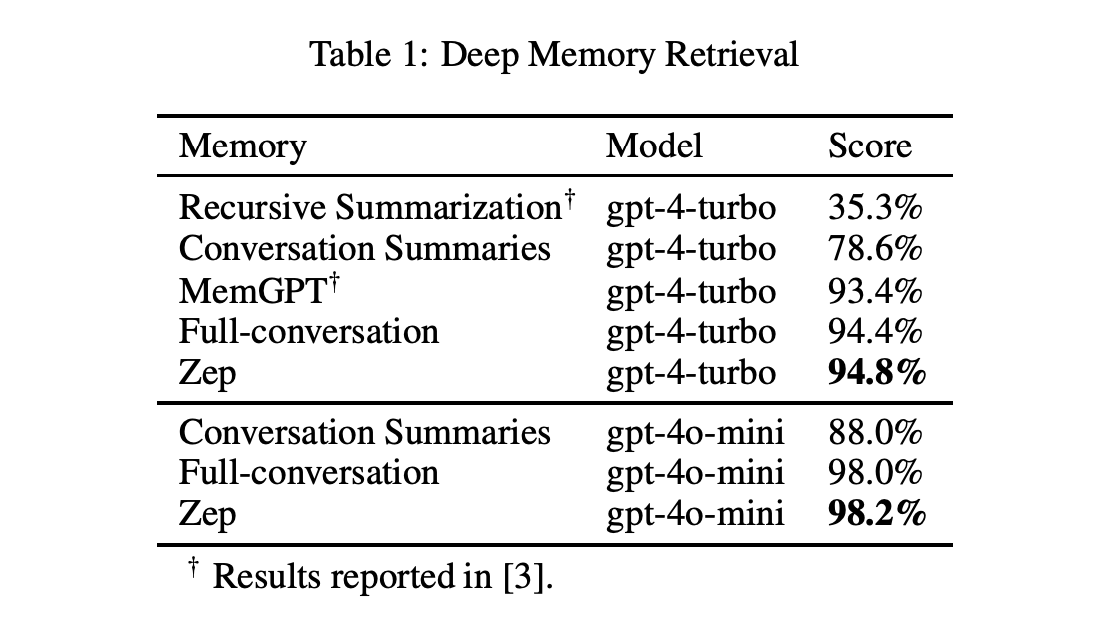
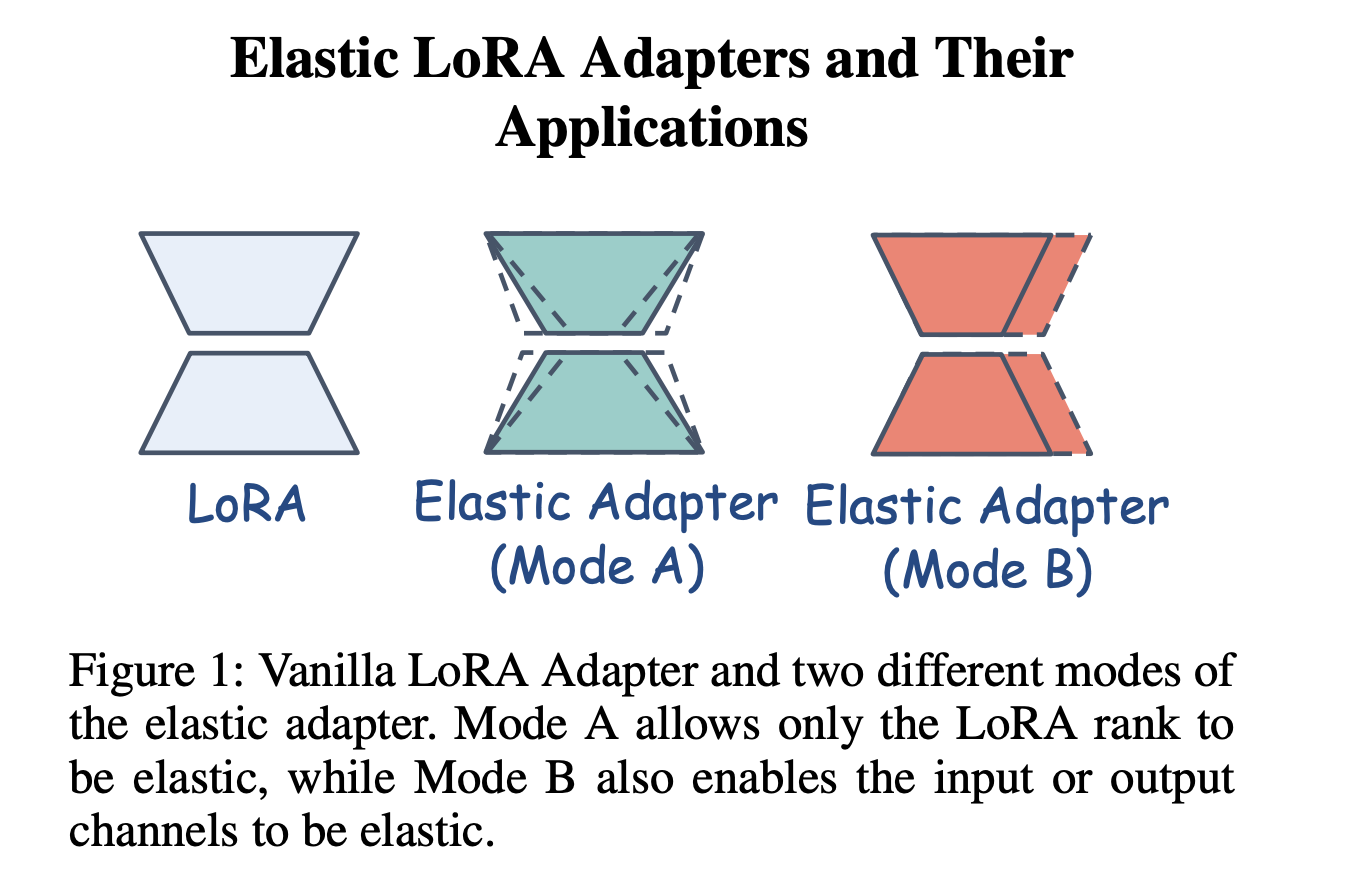
The integration of visual and textual data into artificial intelligence presents a complex challenge. Traditional models often struggle to interpret structured visual documents such as tables, charts, infographics and diagrams with precision. This limitation affects automated content extraction and understanding, which is crucial to applications in data analysis, obtaining information and decision making. As organizations … Read more