Rethinking Audio-based interaction between people and computer
Machines that can respond to human speech with equally expressive and natural sound have become an important target in intelligent interaction systems. Audio language modeling expands this vision by combining speech recognition, natural language understanding and sound generation. Instead of relying on text conversions, models in this room aim to understand and answer using voice alone. This is crucial not only for accessibility and inclusive, but also for achieving more fluid, human -like machine interactions in applications such as voice assistants, sound -based storytelling and hands -free computing.
Limitations of cascaded number pipes
Despite the progress of sound understanding, a clear challenge remains: Most systems still depend on a chain of separate modules for speech-to-text, word processing and text-to-speech conversion. This modular approach can impair performance and responsiveness due to accumulated errors and latency. In addition, these pipelines lack expressive control, making them unfit for nuanced tasks such as emotional dialogue or dynamic speech synthesis. An ideal solution would be a fully unified model capable of understanding an sound question and generating an expressive sound answer directly, eliminating all text -based dissemination.
From token-based models to fully united lalms
Several methods have tried to tackle this. Early approaches, such as Hugginggpt and Audiogpt, used cascaded architectures that combined separate speech and language models. As they expanded the task coverage, these systems fought with real -time voice interaction. Later works, such as Vall-E, Specechgpt, Audio Palm and Qwen2-Audio, introduced token-based systems that convert sound to discreet representations. Still, even these models mostly emit text and require separate vocoders, which limits their ability to produce expressive, immediate sound answers.
Introduction of Step-Audio-Aqaa: an end-to-end AQAA system
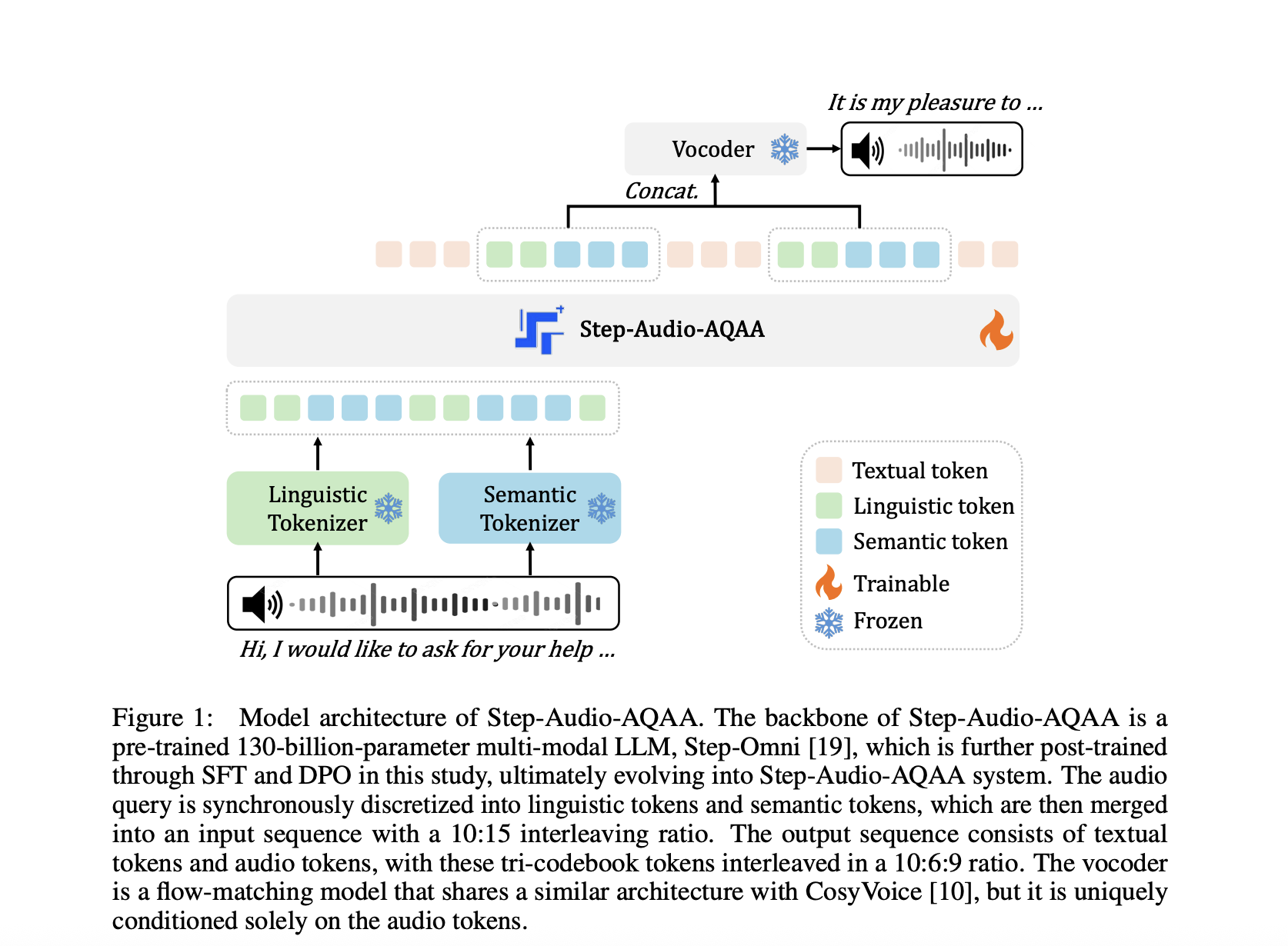
Researchers at Stepfun introduced Step-Audio-Aqaa, a fully end-to-end large sound language model designed specifically for sound request tasks. Unlike previous models, Step-Audio-Aqaa transforms directly input into expressively spoken output without converting it into intermediate text. This architecture combines a double code book-tokenizer, a 130 billion parameter spine llm named Step-Omni and a flow-matching vocoder for natural speech synthesis. The integration of these components enables trouble -free interaction with low latency.
Tokenization, architecture and voice control
The method begins with two separate audio tokenizers – one for linguistic features and another for semantic prosody. The linguistic tokenizer based on para forms extracts structured speech elements such as phonemes at 16.7 Hz using a codebook of 1,024 tokens. Meanwhile, the semantic tokenizer (inspired by COSYVOICE 1.0) cosy acoustic wealth at 25 Hz with 4,096 tokens. These are intertwined in a ratio of 2: 3 and are transferred to step-omni, a multimodal decoder-only LLM trained on text, audio and image data. After this, the model emits tri-code book sequences of audio and text hooks that vocodes are transformed into fluid speech. This setup enables fine -grained voice control, including emotional tone and voice speed.
Benchmark -evaluation and results
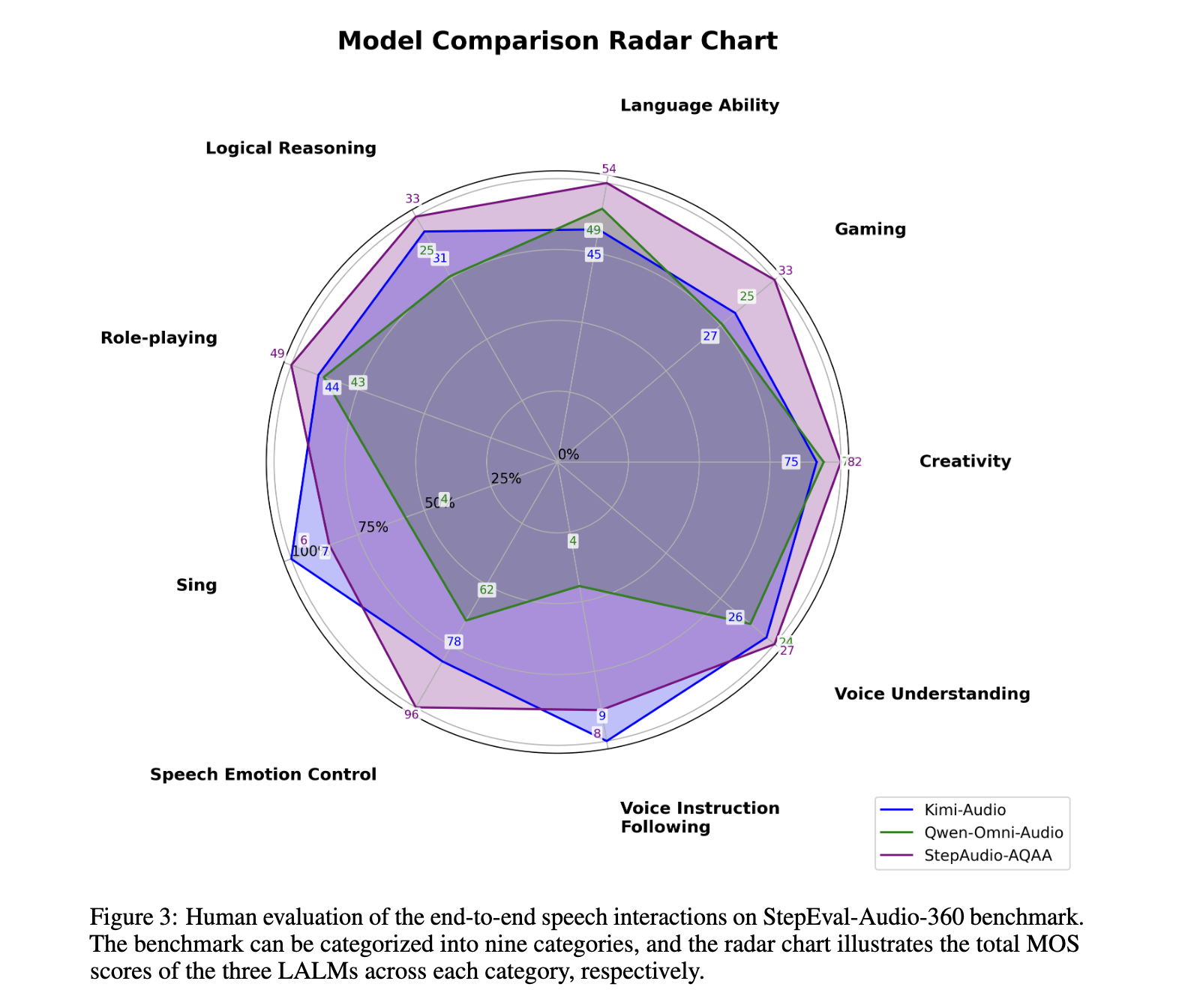
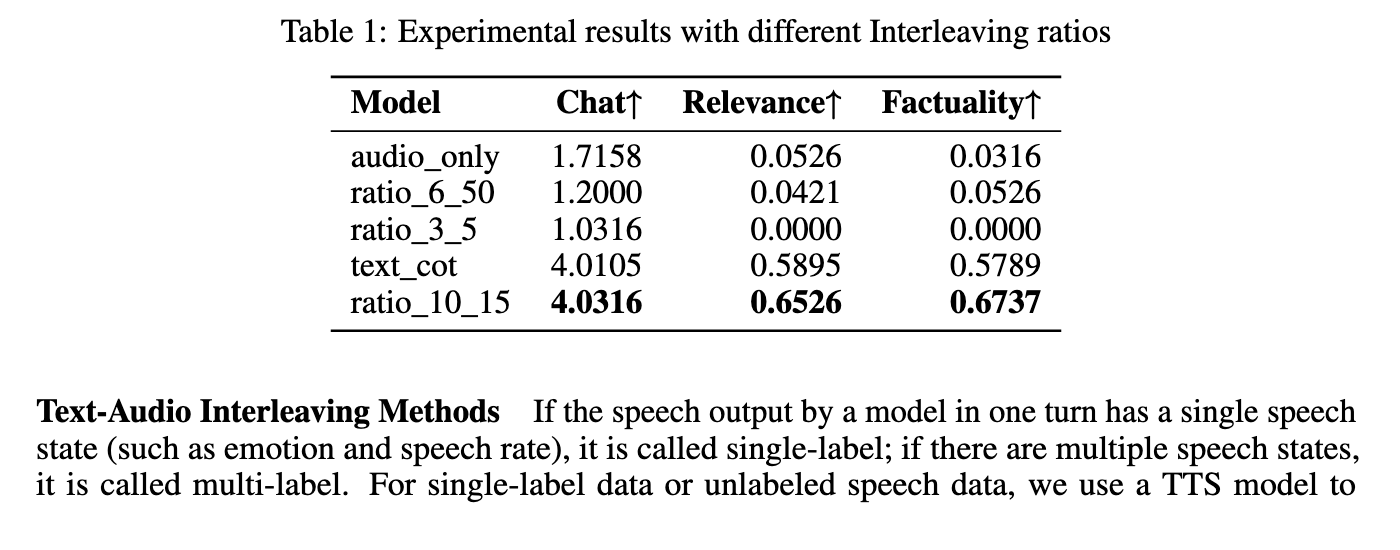
The model was evaluated using Stepeval-Audio-360-Benchmark, which includes multilingual, multidalectal audio tasks across nine categories including creativity, games, emotional management, role-playing and voice understanding. Compared to advanced models such as Kimi-Audio and Qwen-Omni, Step-Audio-Aqaa achieved the highest average results in most categories. Specifically in the text-audio-token relationship experiments, the configuration achieved with a ratio of 10:15 top performance with chat (4.03), relevance (0.65) and factuality (0.67) scores. Among various audio connection techniques performed marker -preserving links best with chat (4.22), relevance (0.57) and factuality (0.57) score. These numbers reflect its strength in generating semantically accurate, emotionally rich and context -conscious soundspons.
Conclusion: Against expressive machine speech
Step-Audio-Aqaa offers a robust solution to the limitations of modular speech treatment pipes. By combining expressive sound tookenization, a powerful multimodal LLM and advanced strategies after training, such as direct preference optimization and model fusion, they succeed in generating high quality, emotionally resonant sound response. This work marks a significant step forward in enabling machines to communicate with speech that is not only functional but expressive and fluid.
Check Paper and model on hug face. All credit for this research goes to the researchers in this project. You are also welcome to follow us on Twitter And don’t forget to join our 100k+ ml subbreddit and subscribe to Our newsletter.
Nikhil is an internal consultant at MarkTechpost. He is pursuing an integrated double degree in materials at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Nikhil is an AI/ML enthusiast who always examines applications in fields such as biomaterials and biomedical science. With a strong background in material science, he explores new progress and creates opportunities to contribute.