Machine learning has been expanded beyond traditional Euclidean spaces in recent years and examined representations in more complex geometric structures. Non-Euklidic representation learning is a growing field that seeks to capture the underlying geometric properties of data by embedding it in hyperbolic, spherical or mixed curvature product spaces. These approaches have been particularly useful for modeling hierarchical, structured or network data more effectively than Euclidean embedders. The field has witnessed significant progress with new tools and algorithms to facilitate these complex representations.
A significant challenge in this domain is the lack of a unified framework that integrates different approaches to non-Euklidic representation learning. Current methods are often spread across multiple software packages, creating inefficiency in implementation. Many existing tools meet specific types of non-Euklidic spaces that limit their wider applicability. Researchers require a comprehensive and accessible library that enables trouble -free embedding, classification and regression while maintaining compatibility with established machine learning frames. Tackling this hole is crucial to promoting non -Euklidic machine learning research and uses.
Several tools have been introduced to facilitate manifold -based machine learning. Geoopt, a Python package, gives Riemannian optimization to non-Euklidic manifolds, but its functionality is limited. Other implementations focus on hyperbolic learning, but lack consistency, resulting in fragmented methods. The absence of an overall tool set with open source bridging these holes has made non-Euklidic machine learning less accessible to a wider research community. A more comprehensive framework is needed to enable even adoption and integration of non-Euklidic learning methods.
A research team from Columbia University introduced Manify, an Open Source Python library designed to tackle the limitations of existing non-Euklidic representation learning tools. Manify extends beyond the current methodologies by incorporating mixed curvature deposits and manifold -based learning techniques in a single package. It is built on geoopt, which improves its abilities by allowing the learning of representations in products of hyperbolic, hypersfair and Euclidean component manifolds. The library facilitates classification and regression tasks, while the estimation of manifold curvature is made possible. By consolidating multiple non-Euklidic learning techniques to a structured framework, Manify provides a robust solution for researchers working with data naturally found in non-Euklidic spaces.
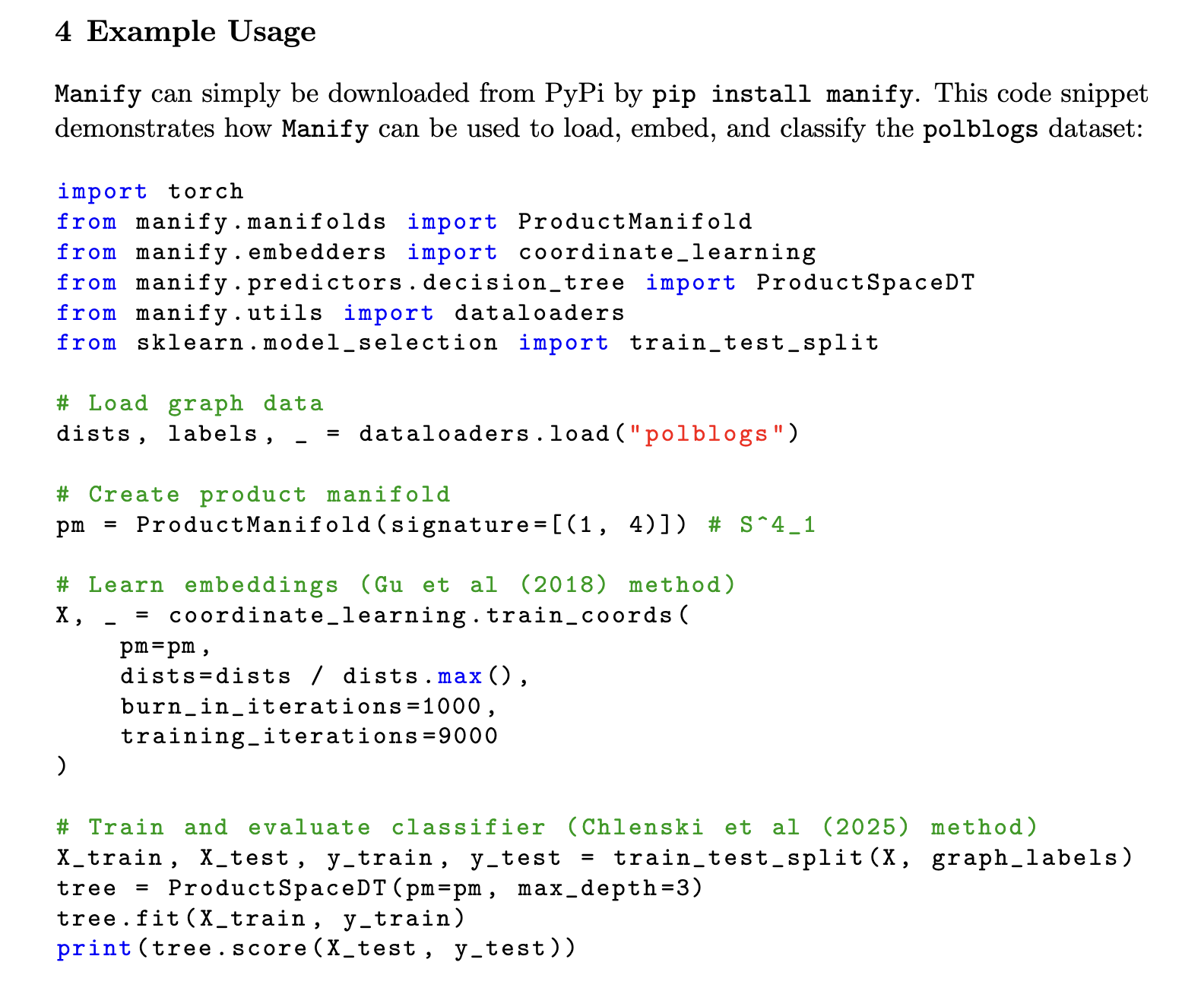
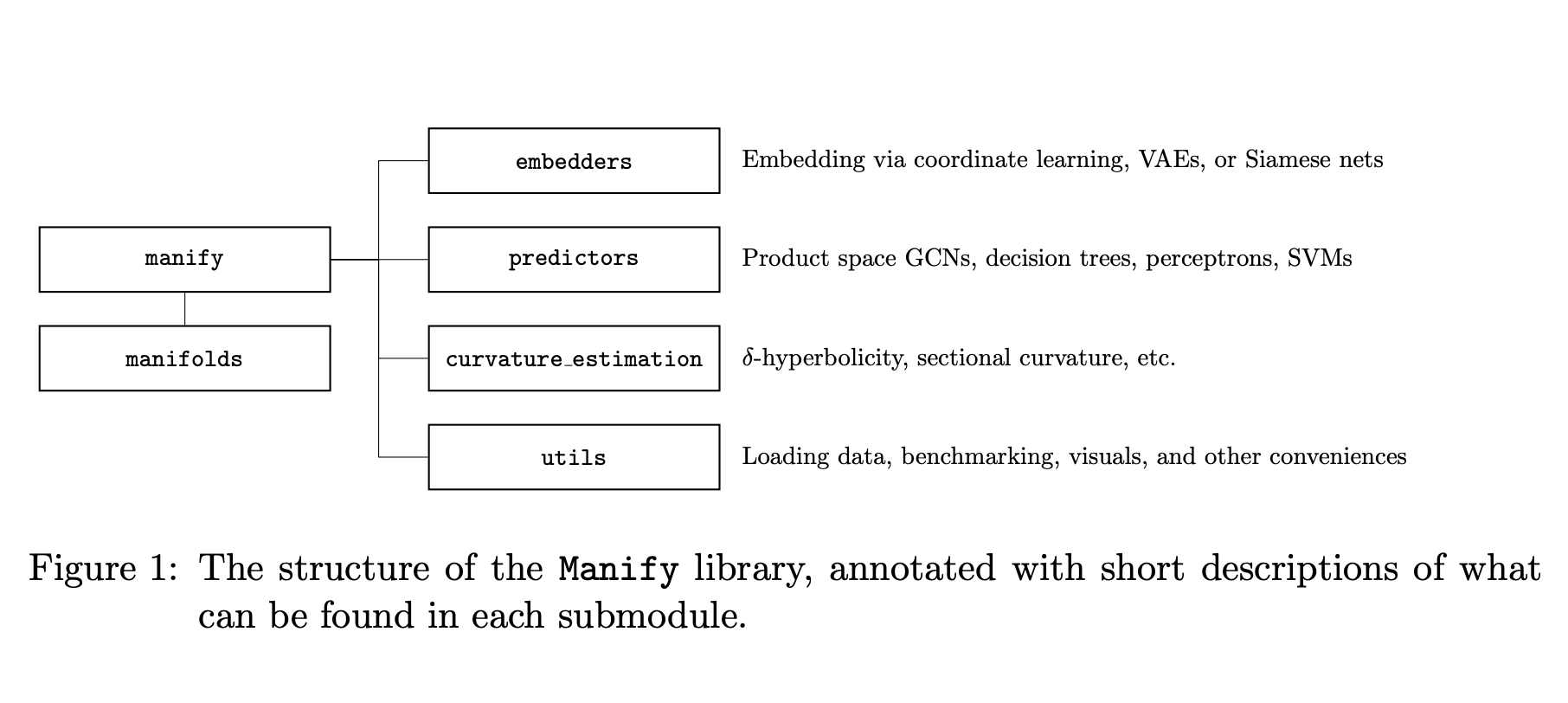
Manification includes three primary functionalities: embedding graphs or spacer matrixes in product manifolds, workouts for manifold-valueed data and estimation of data kit. The library integrates multiple embedding methods, including coordinate learning, Siamese neural networks and variation auto -coders that offer different benefits in different uses. Furthermore, it supports various classifiers, such as decision trees, perceptrons and support vector machines, which have been adapted to work with non-Euklidic data. Manifer also contains specialized tools for measuring curvature, which helps users determine the most appropriate manifold geometry for their data sets. These options make it a versatile and powerful library for researchers examining non-Euklidic learning techniques.
The performance of the manification has been evaluated across multiple machine learning tasks, demonstrating significant improvements in the embedding of quality and predictable accuracy. The library’s ability to model heterogeneous curvature within a single frame has reduced metric distortion compared to Euclidean methods. The results indicate that embedders generated by Manify exhibit superior structural fidelity, and retain distances more accurately than traditional techniques. The library has also shown calculation efficiency, with training times comparable to existing Euclidean-based methods despite the increased complexity of non-Euklidic representations. Performance Benchmarks reveals that Manify achieves an average improvement of about 15% in classification accuracy over Euclidean embedders, showing its effectiveness in manifold -based learning tasks.
Manify represents a great progress in non-Euklidic representation learning, addresses the limitations of existing tools and enables more precise modeling of complex data structures. By offering an open source, well -integrated framework, the library simplifies the adoption of manifold -based learning techniques for researchers and practitioners. The introduction of Manify has overbreaked the gap between theoretical progress and practical implementation, making non-Euklidic learning methods more accessible to the broader scientific community. Future improvements could further optimize its capabilities and solidify its role as a key resource in research in machine learning.
Check out The paper and the github side. All credit for this research goes to the researchers in this project. You are also welcome to follow us on Twitter And don’t forget to join our 80k+ ml subbreddit.
Nikhil is an internal consultant at MarkTechpost. He is pursuing an integrated double degree in materials at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Nikhil is an AI/ML enthusiast who always examines applications in fields such as biomaterials and biomedical science. With a strong background in material science, he explores new progress and creates opportunities to contribute.